HARD DRIVES

A hard drive is a non-volatile hardware component on a computer that acts as the storage for all digital content. It holds program files, documents,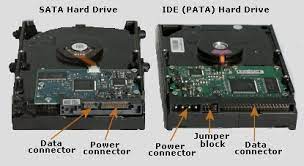 pictures, videos, music, and more. The non-volatile nature of hard drives means they don’t lose data, even if power is lost. Due to this, they help computers store files and other data for a long time – as long as they don’t get damaged or corrupted. Since the first release of hard drives by IBM in 1956, hard drives have evolved from being the size of a refrigerator and having a storage capacity of just 5MB to ones that are pocket-sized and have up to 4 TB of storage capacity.
pictures, videos, music, and more. The non-volatile nature of hard drives means they don’t lose data, even if power is lost. Due to this, they help computers store files and other data for a long time – as long as they don’t get damaged or corrupted. Since the first release of hard drives by IBM in 1956, hard drives have evolved from being the size of a refrigerator and having a storage capacity of just 5MB to ones that are pocket-sized and have up to 4 TB of storage capacity.
Types of Hard Drives
Currently, hard drives are divided into 4 major types:
|
|
These names come from the way they connect to the computer.
Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment (PATA)
The PATA hard drives were first introduced to the market by Compaq and Western Digital in 1986. They can have up to 80GB capacity and transfer data as fast as 133 MB/S. They were named Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment because they use a parallel ATA interface to connect to the computer. Apart from PATA, they are also called Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) and Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics (EIDE).
PATA hard drives are made of mechanical moving parts and are based on parallel signaling technology – meaning they transmit multiple bits of data simultaneously.
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
In recent times, a lot of desktop and laptop computers have gotten SATA hard drives because they have superseded PATA hard drives in size, power consumption, and even better pricing.
The mode of connection to a computer remains the same as PATA, but instead of parallel signaling technology for data transmission, they use serial signaling technology. This means that they transfer data one bit at a time.
A notable advantage SATA hard drives have over PATA hard drives is the transmission of data at a rate of 150 – 300 MB/S. In addition, they have thinner cables and a cable limit of 1 meter.
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI)
SCSI hard drives are upgrades over SATA and PATA drives for many reasons such as round-the-clock operations, speed, storage, and several others.
For connection, SCSI hard drives use a small computer system interface – which is a standard for connecting peripheral devices such as printers, scanners, and others.
Best of all, they allow the connection of peripheral devices such as printers, scanners, and other hard drives. In addition, they transmit data at 320 MB/S and you can connect them internally or externally.
Connections through SCSI on personal computers have now been replaced by the Universal Serial BUS (USB). This means that SCSI is no longer used as consumer hardware.
Solid State Drive (SSD)
SSD hard drives are one of the latest hard drive technologies at the time of writing this article.
Unlike the hard drive technologies before SSD drives, they don’t consist of moving parts and they don’t use magnetism for storing data.
Instead, they use integrated circuits (ICs) just like third-generation computers. This makes them more durable, faster, and less prone to damage and corruption.
SSD hard drives have a notable advantage of transferring data at speed of 550 MB/S and allow faster boot times than the types of hard drives before them.
Conclusion:
From PATA to SATA, SCSI and SSD, hard drives continue to evolve and research to make better ones is ongoing.
In fact, there is a new variation of SSD hard drives called NVMe (Non-volatile Memory Express) SSDs that has the capacity to transfer data as fast as 3.5 GB/S. This makes them the best choice for video editing and high-resolution gaming, though they require more power than the actual SSDs.

