Differences between a Hub, a Switch, and a Router

28 July, 2021
In networking, the terms switches, hubs, and routers are sometimes used interchangeably which is wrong. Despite them being similar, there are differences in how they handle data. These three components may be integrated into a single device making it hard for a student to distinguish between them.
Hub vs Switch vs Router
In network equipment and devices, data is usually transmitted in the form of a frame. When a frame is received, it is amplified and then transmitted to the port of the destination PC (Personal Computer). The big difference between hub and switch is in the method in which frames are being delivered.
Unlike an Ethernet hub or switch that is concerned with transmitting frames, a router is to route packets to other networks until that packet ultimately reaches its destination. One of the key features of a packet is that it not only contains data, but the destination addresses of where it's going. What's more, router is the only one of these three devices that will allow you to share a single IP (Internet Protocol) address among multiple network clients.
What is a Switch?
A switch is a multicast networking device that works under the Datalink layer of the OSI model and connects a bunch of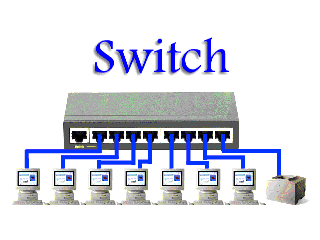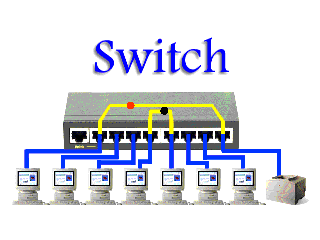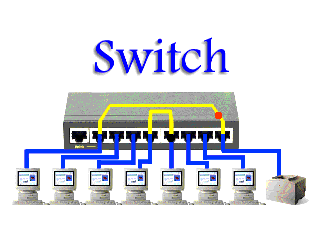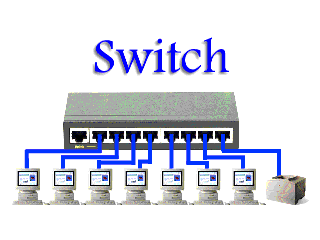 computers or devices in a network. It’s mainly used to send a private message and it does not waste data.
computers or devices in a network. It’s mainly used to send a private message and it does not waste data.
 computers or devices in a network. It’s mainly used to send a private message and it does not waste data.
computers or devices in a network. It’s mainly used to send a private message and it does not waste data.A switch can easily identify which device is connected to which port by using a MAC address giving it the ability to deliver the message to a particular machine.
| Advantages of using a Switch | Disadvantages of using Switches |
|
|
What is a Hub?
A Hub is a simple and cheap networking device that works under the physical layer of the OSI model and connects a bunch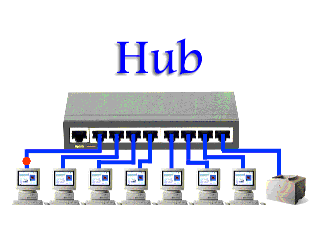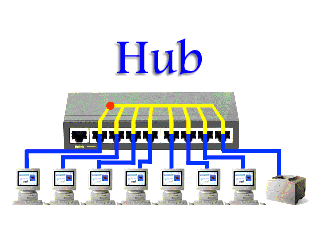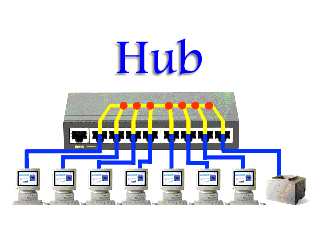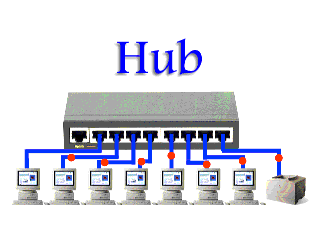 of computers in a Local Area Network (LAN). It is considered less intelligent because it does not filter data and does not know where the data is to be sent.
of computers in a Local Area Network (LAN). It is considered less intelligent because it does not filter data and does not know where the data is to be sent.
 of computers in a Local Area Network (LAN). It is considered less intelligent because it does not filter data and does not know where the data is to be sent.
of computers in a Local Area Network (LAN). It is considered less intelligent because it does not filter data and does not know where the data is to be sent.All information sent to a hub is automatically sent to all ports of the devices connected to it. This leads to wastage of bandwidth.
| Advantages of using a Hub | Disadvantages of using a Hub |
|
|
What is a Router?
A Router is a networking device that operates under the network layer of the OSI model and is used to connect two or more networks. It is a device that establishes a common link between networks to enable data flow between them. The router is generally located at gateways, the places where two or more networks connect. Using headers and forwarding tables, router determines the best path to forward the packets. In addition, router uses protocols such as ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to communicate with each other and configures the best route between any two hosts. In a word, router forwards data packets along with networks.
common link between networks to enable data flow between them. The router is generally located at gateways, the places where two or more networks connect. Using headers and forwarding tables, router determines the best path to forward the packets. In addition, router uses protocols such as ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to communicate with each other and configures the best route between any two hosts. In a word, router forwards data packets along with networks.
 common link between networks to enable data flow between them. The router is generally located at gateways, the places where two or more networks connect. Using headers and forwarding tables, router determines the best path to forward the packets. In addition, router uses protocols such as ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to communicate with each other and configures the best route between any two hosts. In a word, router forwards data packets along with networks.
common link between networks to enable data flow between them. The router is generally located at gateways, the places where two or more networks connect. Using headers and forwarding tables, router determines the best path to forward the packets. In addition, router uses protocols such as ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to communicate with each other and configures the best route between any two hosts. In a word, router forwards data packets along with networks.| Advantages of using a Router | Advantages of using a Router |
|
|
